Cobalt(II) oxide
Cobalt(II) oxide is an inorganic compound that has been described as an olive-green[3] or gray[4] solid.
It is used extensively in the ceramics industry as an additive to create blue-colored glazes and enamels, as well as in the chemical industry for producing cobalt(II) salts.
A related material is cobalt(II,III) oxide, a black solid with the formula Co3O4.
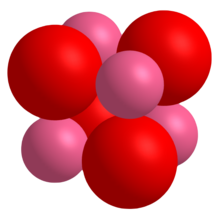
CoO crystals adopt the periclase (rock salt) structure with a lattice constant of 4.2615 Å.
[3][4] Cobalt(II,III) oxide decomposes to cobalt(II) oxide at 950 °C:[7] It may also be prepared by precipitating the hydroxide, followed by thermal dehydration:[citation needed] As can be expected, cobalt(II) oxide reacts with mineral acids to form the corresponding cobalt salts:[citation needed] Cobalt(II) oxide has for centuries been used as a coloring agent on kiln fired pottery.