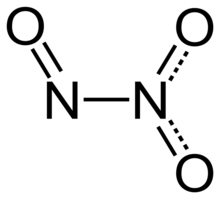
Dinitrogen trioxide
It forms upon mixing equal parts of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide and cooling the mixture below −21 °C (−6 °F):[4] Dinitrogen trioxide is only isolable at low temperatures (i.e., in the liquid and solid phases).
This isomer can be produced from the reaction of tetrabutylammonium nitrite and triflic anhydride in dichloromethane solution at -30°C.
Nitrite salts are sometimes produced by adding N2O3 to water solutions of bases: Typically, N–N bonds are similar in length to that in hydrazine (145 pm).
Some other nitrogen oxides also possess long N–N bonds, including dinitrogen tetroxide (175 pm).
Similar to nitronium nitrate, this molecule can also co-exist in equilibrium with an ionic gas called nitrosonium nitrite ([NO]+[NO2]–) [7]