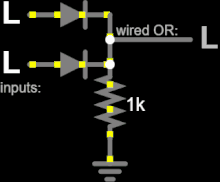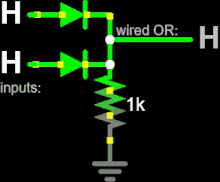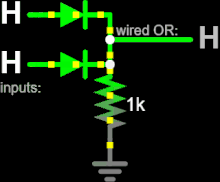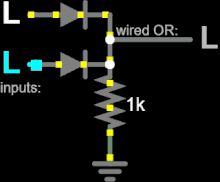
Diode logic
Diode logic can only implement OR and AND, because inverters (NOT gates) require an active device.
Switching between active-high and active-low is commonly used to achieve a more efficient logic design.
The diode symbol's arrow shows the forward-biased direction of conventional current flow.
At least one input of every gate must be connected to a strong-enough high or low voltage source.
If all inputs are disconnected from a strong source, the output may not fall within a valid voltage range.
The capacitance between anode and cathode is inversely proportional to the reverse voltage, growing as it approaches 0 volts and into forward bias.
There is also a recovery concern: a diode's current will not decrease immediately when switching from forward-biased to reverse-biased, because discharging its stored charge takes a finite amount of time (trr or reverse recovery time).
The recovery time of the very slow selenium diodes caused a glitch on the inverter output.
This level restoration allows more cascaded logic stages and removes noise, facilitating very large scale integration.
[citation needed] Low-impedance push–pull outputs of conventional ICs shouldn't directly be connected to external circuitry, as they may create a short circuit between power and ground.
[4] A variant approach suggests keeping a supply of 1N914 diodes with inverting Schmitt trigger ICs to provide hysteresis and functional completeness.
[6] During the 1960s the use of tunnel diodes in logic circuits was an active research topic.
When compared to transistor logic gates of the time, the tunnel diode offered much higher speeds.
More complex gates, with additional tunnel diodes and bias power supplies, overcame some of these limitations.