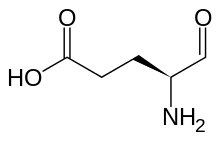
Glutamate-1-semialdehyde
Glutamate-1-semialdehyde is a molecule formed from by the reduction of tRNA bound glutamate, catalyzed by glutamyl-tRNA reductase.
It is isomerized by glutamate-1-semialdehyde 2,1-aminomutase to give aminolevulinic acid in the biosynthesis of porphyrins, including heme and chlorophyll.
[1][2]
This biochemistry article is a stub.
You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.