Hurricane Elsa
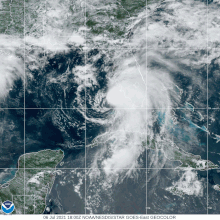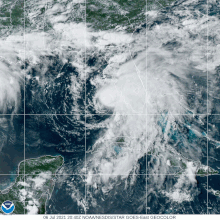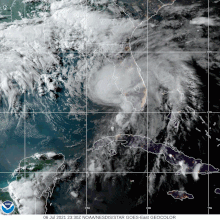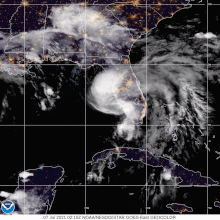
The storm strengthened to a hurricane around 12:00 UTC on July 2, as its center moved just south of Barbados, and then reached its peak intensity six hours later with maximum 1-minute sustained winds of 85 mph (140 km/h) and a minimum central pressure of 991 mbar (29.3 inHg), about 95 mi (155 km) west-northwest of Saint Vincent.
The wave produced disorganized showers and thunderstorms during the next few days, before a closed and well-defined low pressure system developed by 18:00 UTC on June 30, marking the formation of a tropical depression about 1,150 mi (1,850 km) east-southeast of Barbados.
The potential for tropical cyclone formation within the wave was first noted by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) at 12:00 UTC on June 29, and initially given a low (less than 40%) chance of development over the next five days.
[12] Six hours later, Elsa reached its peak intensity with maximum 1-minute sustained winds of 85 mph (140 km/h) and a minimum central pressure of 991 mbar (29.3 inHg), while located about 95 mi (155 km) west-northwest of Saint Vincent.
Elsa's forward speed increased while it moved across the eastern and central Caribbean Sea early on July 3, but the low-level center became exposed to the west of the main area of deep convection, and it weakened into a tropical storm about 115 mi (185 km) south of the southern coast of the Dominican Republic.
[1] The storm continued to lose strength later that day and early on July 4, as the center passed offshore but near the mountainous terrain of southwestern Haiti and then just north of Jamaica.
[13][14] An Air Force Reserve reconnaissance aircraft investigating Elsa late on July 4, found it to be undergoing a convective burst and beginning to restrengthen.
[15] At 18:00 UTC on July 5, Elsa made landfall on the south coast of Cuba in Cienaga de Zapata National Park with maximum winds of about 65 mph (100 km/h).
[21] In Barbados, marine and flash flood advisories were posted on the island by June 30, in addition to the tropical cyclone watches and warnings by the meteorological service of the country.
[29] The island country was also in a lockdown as the people there rush to protect their homes and buy food supplies ahead of the hurricane while 54 native individuals in the area were brought in evacuation shelters to ride out the storm.
[34] Elsa threatened the Windward Islands during the 2021 eruption of La Soufrière on St. Vincent, with interests in the region being asked to monitor for official updates.
[40] Businesses, schools and other public utilities were instructed to temporarily close due to the hurricane, except essential workers such as police, health services and others which has to remain alert under their departments.
[51] A few hours later, a Tropical Storm Watch was ordered for the Dominican Republic from the border with Haiti eastward to Punta Palenque, as well as the entire island of Jamaica.
Also in the Dominican Republic, a Tropical Storm Watch was put in place from Cape Engaño to Bahia de Manzanillo on the northern coast of the country.
The Ministry of Rural Development and Local Government released reports of downed trees and flooding across Port of Spain, Diego Martin, San Juan–Laventille, Sangre Grande, Couva–Tabaquite–Talparo, Mayaro–Rio Claro, and Siparia.
As a result, water supply was affected in Arima, El Dorado, Matura, Maracas, Tacarigua, Toco, Saint Joseph, and Valencia.
[97] In the Dominican Republic, strong winds caused by Elsa toppled walls in houses in southwestern Baoruco Province, resulting in two separate fatalities of a 15-year-old boy and 75-year-old woman on July 3.
[99] In San José de Ocoa Province, due to the swelling of the Nizao River, 3 houses were damaged by floods, while the communities of La Estretchura, Monte Negro, and Quitasueño were cut off.
[109] The Municipal Defense Council of Pilón reported damage to agriculture and several homes due to mudslides caused by flooding in the mountains of the province.
[110] A dam in Pilón also reportedly overflowed due to the region accumulating 121.6 mm (4.79 in) of rain, according to the National Institute of Hydraulic Resources in Granma.
[116] The towns of Jiabcoa, Santa Clara and Arroyo Pretiles were cut off by the flooding of the Jibacoa River caused by Elsa when over 122 mm (4.8 in) of rain fell in 3 hours.
The crew of the Cyprus flagged bulk carrier ship Western Carmen contacted the United States Coast Guard in Key West at approximately 17:30 UTC to report they had found 4 people in the water.
The Coast Guard responded and sent out both air and surface assets to scour for survivors, the searches covered about 7,459 square miles (12,148 km) of water for 192 hours.
The Coast Guard rescued 5 more victims from the water, but at 02:00 UTC on July 9, the force suspended its search for the remaining 9 passengers,[118] which were later presumed dead.
[127] Rains from Elsa soaked the rubble of the Surfside condo collapse, and lightning forced workers to stop searching for bodies and survivors for two hours early on July 6.
[129] A high-end EF1 tornado also struck the eastern side of Jacksonville, starting in the San Jose neighborhood of the city and travelled all the way to the Phillips Highway area.
On July 7, in Camden County, the storm produced an EF1 tornado that struck St. Marys, ripping an exterior wall off of a house before moving through an RV park at Naval Submarine Base Kings Bay.
The Oyster Bay branch of the Long Island Rail Road was suspended on July 9 due to fallen trees east of Roslyn.
[144] In Rhode Island, the Department of Environmental Management warned residents of rip currents even after Elsa became extratropical, due to higher tides.
[149] Duke Energy, the main electric company in the Tampa Bay area, stated that it had about 3,000 employees, contractors, tree specialists and support personnel ready to respond power outages.

Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown