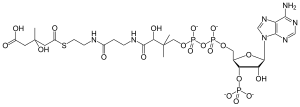
HMG-CoA
β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways.
The research of Minor J. Coon and Bimal Kumar Bachhawat in the 1950s at University of Illinois led to its discovery.
Mevalonate synthesis begins with the beta-ketothiolase-catalyzed Claisen condensation of two molecules of acetyl-CoA to produce acetoacetyl CoA.
[8] In the final step of mevalonate biosynthesis, HMG-CoA reductase, an NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase, catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA into mevalonate, which is the primary regulatory point in this pathway.
Mevalonate serves as the precursor to isoprenoid groups that are incorporated into a wide variety of end-products, including cholesterol in humans.