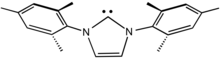
IMes
IMes is an abbreviation for an organic compound that is a common ligand in organometallic chemistry.
The compound, a white solid, is often not isolated but instead is generated upon attachment to the metal centre.
In the presence of acid, the resulting glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine) condenses with formaldehyde to give the dimesitylimidazolium cation.
[5] Some variants of IMes and IPr have saturated backbones, two such ligands are SIMes and SIPr.
[1] They are prepared by alkylation of substituted anilines with dibromoethane followed by ring closure and dehydrohalogenation of the dihydroimidazolium salt.