Inositol
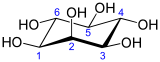
In biochemistry, medicine, and related sciences, inositol generally refers to myo-inositol (formerly meso-inositol), the most important stereoisomer of the chemical compound cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol.
In myo-inositol, two of the hydroxyls, neither adjacent not opposite, lie above the respective hydrogens relative to the mean plane of the ring.
It is one of the most ancient components of living beings with multiple functions in eukaryotes, including structural lipids and secondary messengers.
The highest concentration is in the brain, where it plays an important role in making other neurotransmitters and some steroid hormones bind to their receptors.
[4] In other tissues, it mediates cell signal transduction in response to a variety of hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors and participates in osmoregulation.
However, since all other isomers are meso (non-chiral) compounds, the name myo-inositol is now preferred (myo- being a medical prefix for "muscle").
[11] myo-Inositol plays an important role as the structural basis for a number of secondary messengers in eukaryotic cells, the various inositol phosphates.
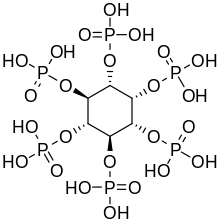
[6] Inositol hexaphosphate, also called phytic acid or IP6, is a phytochemical and the principal storage form of phosphorus in many plant tissues, especially bran and seed.
[17] In plants, the hexaphosphate of inositol, phytic acid or its salts, the phytates, serve as phosphate stores in seed, for example in nuts and beans.
Inositol, phosphatidylinositol, and some of their mono- and polyphosphates function as secondary messengers in a number of intracellular signal transduction pathways.
[31] Inositol should not be routinely implemented for the management of preterm babies who have or are at a risk of infant respiratory distress syndrome (RDS).
[36] myo-Inositol's role as FSH second messenger leads to a correct ovarian follicle maturation and consequently to a higher oocyte quality.
Improving the oocyte quality in both women with or without PCOS, myo-inositol can be considered as a possible approach for increasing the chance of success in assisted reproductive technologies.
[12] Recent evidence reports a faster improvement of the metabolic and hormonal parameters when these two isomers are administered in their physiological ratio.
[43] New evidence regarding PCOS aetiopathogenesis describes an alteration in the species and the quantity of each strain characterizing the normal gastrointestinal flora.
[46] Inositol has been used as an adulterant or cutting agent for many illegal drugs, such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and sometimes heroin,[47] probably because of its solubility, powdery texture, or reduced sweetness (50%) compared to more common sugars.
[50] It is also present in beans, nuts, and grains, however, these contain large amounts of myo-inositol in the phytate form, which is not bioavailable without transformation by phytase enzymes.
[3] Another route is microbial fermentation of carbohydrates by various organisms, such as the fungus Neurospora crassa (Beadle and Tatum, 1945), Candida boidini (Shirai et al., 1997), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Culbertson et al., 1976), Escherichia coli (Hansen, 1999).
[3] Alternatively, enzyme extracts from microbial cultures can be used in vitro to obtain myo-inositol from various substrates, including glucose, sucrose, starch, xylose, and amylose.