Lipid metabolism
Lipid catabolism is accomplished by a process known as beta oxidation which takes place in the mitochondria and peroxisome cell organelles.
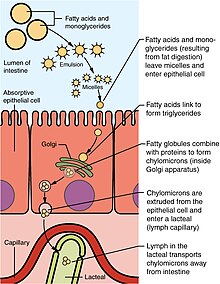
Digestion is the first step to lipid metabolism, and it is the process of breaking the triglycerides down into smaller monoglyceride units with the help of lipase enzymes.
Ingested cholesterol is not broken down by the lipases and stays intact until it enters the epithelium cells of the small intestine.
[11] It is the pancreatic lipase that is responsible for signalling for the hydrolysis of the triglycerides into separate free fatty acids and glycerol units.
Short chain fatty acids can be absorbed in the stomach, while most absorption of fats occurs only in the small intestines.
Once the triglycerides are broken down into individual fatty acids and glycerols, along with cholesterol, they will aggregate into structures called micelles.
Fatty acids and monoglycerides leave the micelles and diffuse across the membrane to enter the intestinal epithelial cells.
In the cytosol of epithelial cells, triglycerides and cholesterol are packaged into bigger particles called chylomicrons which are amphipathic structures that transport digested lipids.
[6][2][3] Due to the hydrophobic nature of membrane lipids, triglycerides and cholesterols, they require special transport proteins known as lipoproteins.
[14] Triglycerides will get broken down into fatty acids and glycerol before entering cells and remaining cholesterol will again travel through the blood to the liver.
The main products of the beta oxidation pathway are acetyl-CoA (which is used in the citric acid cycle to produce energy), NADH and FADH.
The overall net reaction, using palmitoyl-CoA (16:0) as a model substrate is: In addition to dietary fats, storage lipids stored in the adipose tissues are one of the main sources of energy for living organisms.
[citation needed] Lipid metabolism is tightly regulated by hormones to ensure a balance between energy storage and utilization.
[23] A good deal of the time these disorders are hereditary, meaning it's a condition that is passed along from parent to child through their genes.
![[15] Breakdown of fatty acids by beta oxidation](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/cb/Beta_oxidation_of_palmitic_acid.jpg/705px-Beta_oxidation_of_palmitic_acid.jpg)