List of ancient Iranian peoples
They divided into "Western" and "Eastern" branches from an early period, roughly corresponding to the territories of Persia and Scythia, respectively.
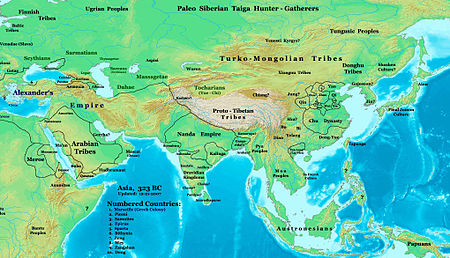
By the 1st millennium BCE, Medes, Persians, Bactrians and Parthians populated the Iranian plateau, while others such as the Scythians, Sarmatians, Cimmerians and Alans populated the steppes north of the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, as far as the Great Hungarian Plain in the west.
[1] Ancient Iranian peoples lived in many regions and, at about 200 BC, they had as farthest geographical points dwelt by them: to the west the Great Hungarian Plain (Alföld), east of the Danube river (where they formed an enclave of Iranian peoples), Ponto-Caspian steppe in today's southern Ukraine, Russia and far western Kazakhstan, and to the east the Altay Mountains western and northwestern foothills and slopes and also western Gansu, Ordos Desert, and western Inner Mongolia, in northwestern China(Xinjiang), to the north southern West Siberia and southern Ural Mountains (Riphean Mountains?)
[1] During Late Antiquity, in a process that lasted until Middle Age, the Iranian populations of Scythia and Sarmatia, in the western (Ponto-Caspian) and central (Kazakh) Eurasian Steppe and most of Central Asia (that once formed a large geographic area dwelt by Iranian peoples), started to be conquered by other non-Iranian peoples and began to be marginalized, assimilated or expelled mainly as result of the Turkic peoples conquests and migrations that resulted in the Turkification of the remaining Iranian ethnic groups in Central Asia and the western Eurasian steppe.
Germanic, Slavic and later Mongolian conquests and migrations also contributed to the decline of the Iranian peoples in these regions.