Fries rearrangement
In the first reaction step a Lewis acid for instance aluminium chloride AlCl3 co-ordinates to the carbonyl oxygen atom of the acyl group.
A low reaction temperature favors para substitution and with high temperatures the ortho product prevails, this can be rationalised as exhibiting classic thermodynamic versus kinetic reaction control as the ortho product can form a more stable bidentate complex with the aluminium.
In all instances only esters can be used with stable acyl components that can withstand the harsh conditions of the Fries rearrangement.
If the aromatic or the acyl component is heavily substituted then the chemical yield will drop due to steric constraints.
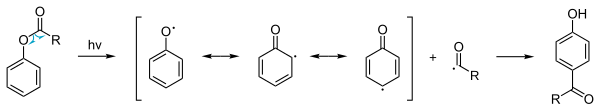
The photo-Fries rearrangement can likewise give [1,3] and [1,5] products,[7][8] which involves a radical reaction mechanism.
However, photo-Fries rearrangement may occur naturally, for example when a plastic object made of aromatic polycarbonate, polyester or polyurethane, is exposed to the sun (aliphatic carbonyls undergo Norrish reactions, which are somewhat similar).