Controlled-access highway
On the controlled-access highway, opposing directions of travel are generally separated by a median strip or central reservation containing a traffic barrier or grass.
Modern controlled-access highways originated in the early 1920s in response to the rapidly increasing use of the automobile, the demand for faster movement between cities and as a consequence of improvements in paving processes, techniques and materials.
The Bronx River Parkway was the first road in North America to utilize a median strip to separate the opposing lanes, to be constructed through a park and where intersecting streets crossed over bridges.
[17] In Canada, the first precursor with semi-controlled access was The Middle Road between Hamilton and Toronto, which featured a median divider between opposing traffic flow, as well as the nation's first cloverleaf interchange.
This highway developed into the Queen Elizabeth Way, which featured a cloverleaf and trumpet interchange when it opened in 1937, and until the Second World War, boasted the longest illuminated stretch of roadway built.
[19] Thus, as originally conceived, a freeway is simply a strip of public land devoted to movement to which abutting property owners do not have rights of light, air or access.
Some countries, such as the United Kingdom, do not distinguish between the two, but others make a distinction; for example, Germany uses the words Kreuz ("cross") or Dreieck ("triangle") for the former and Ausfahrt ("exit") for the latter.
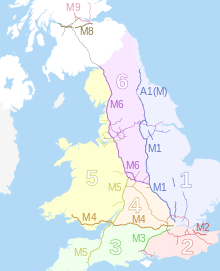
A few of the more common types of junction are shown below:[30][31][32] There are many differences between countries in their geography, economy, traffic growth, highway system size, degree of urbanization and motorization, etc.
[citation needed] In Italy, a study performed on urban motorway A56 Tangenziale di Napoli showed that reduction of speed leads to a decrease in accidents.
This has had the benefit of not creating heavily trafficked surface roads and, in the case of Melbourne's EastLink freeway, prevented the destruction of an ecologically sensitive area.
All of the tunnels are designed to act as an inner-city ring road or bypass system and include provision for public transport, whether underground or in reclaimed space on the surface.
[58] However, freeways are not beneficial for road-based public transport services, because the restricted access to the roadway means that it is awkward for passengers to get to the limited number of boarding points unless they drive to them, largely defeating the purpose.
[59] In Canada, the extension of Highway 401 toward Detroit, known as the Herb Gray Parkway, has been designed with numerous tunnels and underpasses that provide land for parks and recreational uses.
[60][61] Urban planning experts such as Drusilla Van Hengel, Joseph DiMento and Sherry Ryan argue that although properly designed and maintained freeways may be convenient and safe, at least in comparison to uncontrolled roads, they may not expand recreation, employment and education opportunities equally for different ethnic groups, or for people located in certain neighborhoods of any given city.
One of the foremost rationales for the creation of the United States Department of Transportation (USDOT) was that an agency was needed to mediate between the conflicting interests of interstates and cities.
[64] At present, freeway expansion has largely stalled in the United States, due to a multitude of factors that converged in the 1970s: higher due process requirements prior to taking of private property, increasing land values, increasing costs for construction materials, local opposition to new freeways in urban cores, the passage of the National Environmental Policy Act (which imposed the requirement that each new federally funded project must have an environmental impact statement or report) and falling gas tax revenues as a result of the nature of the flat-cent tax (it is not automatically adjusted for inflation), the tax revolt movement,[65] and growing popular support for high-speed mass transit in lieu of new freeways.
In Northern Ireland a distinct numbering system is used, which is separate from the rest of the United Kingdom, though the classification of roads along the lines of A, B and C is universal throughout the UK and the Isle of Man.
It has a small portion serving Antiguo Cuscatlán, La Libertad, and merges with the RN-5 (East–West, Boulevard de Los Proceres/Autopista del Aeropuerto) in San Salvador.
The advantage of grade-separated interchanges is that freeway drivers can almost always maintain their speed at junctions since they do not need to yield to vehicles crossing perpendicular to mainline traffic.
Iraq's network of highways connects it from the inside to neighboring countries such as Syria, Turkey, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Jordan and Iran.
Currently, most of the expressways in Vietnam are four-lane highways, with some routes like Ha Noi - Haiphong, and Phap Van - Cau Gie being six-lane.
[24] Nonetheless, some specific conditions provide a height risk of a more severe accidents, such as: Highways in Albania form part of the recent Albanian road system.
Austria currently has 18 Autobahnen, since 1982 built and maintained by the self-financed ASFiNAG stock company in Vienna, which is wholly owned by the Austrian republic and earns revenue from road-user charges and tolls.
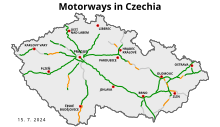
Unusually for European countries, interchanges (between motorways called Knoten, "knots") are numbered by distance in kilometres starting from where the route begins; this arrangement is also used in the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Spain, and most provinces of Canada (and in most American states, albeit in miles).
The primary high-speed motorways in Croatia are called autoceste (singular: autocesta; Croatian pronunciation: [ˈaʊtotsesta]), and they are defined as roads with at least two lanes in each direction (including hard shoulder) and a speed limit of not less than 80 km/h (50 mph).
Under the Transport 21 infrastructural plan,[126] motorways or high quality dual carriageways were built between Dublin and the major cities of Cork, Galway, Limerick and Waterford by the end of 2010.
The first stage in this process occurred when all the HQDC schemes open or under construction on the N7 and N8, and between Kinnegad and Athlone on the N6 and Kilcullen and south of Carlow on the N9, were reclassified motorway on 24 September 2008.
Legal provisions allow operators to set the limit to 150 km/h (95 mph) on their concessions on a voluntary basis if there are three lanes in each direction and a working SICVE, or Safety Tutor, which is a speed-camera system that measures the average speed over a given distance.
Therefore, since 1979 large portions of the motorway network have been equipped with variable message signs and dynamic electronic displays, both of which are aspects of intelligent transportation systems.
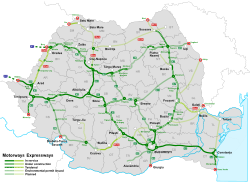
[146] The Romanian Government has adopted a General Master Plan for Transport that was approved by the European Union in July 2015, containing the strategy for expanding the road (including motorway) network until 2040, using EU funding.