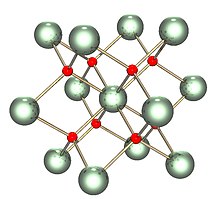
Uranium dioxide
The solid is isostructural with (has the same structure as) fluorite (calcium fluoride), where each U is surrounded by eight O nearest neighbors in a cubic arrangement.
[citation needed] Uranium oxide (urania) was used to color glass and ceramics prior to World War II, and until the applications of radioactivity were discovered this was its main use.
Casks can be also made of DUO2-steel cermet, a composite material made of an aggregate of uranium dioxide serving as radiation shielding, graphite and/or silicon carbide serving as neutron radiation absorber and moderator, and steel as the matrix, whose high thermal conductivity allows easy removal of decay heat.
[citation needed] Depleted uranium dioxide can be also used as a catalyst, e.g. for degradation of volatile organic compounds in gaseous phase, oxidation of methane to methanol, and removal of sulfur from petroleum.
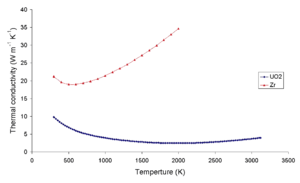
In earlier times, uranium dioxide was also used as heat conductor for current limitation (URDOX-resistor), which was the first use of its semiconductor properties.
[citation needed] Uranium dioxide displays strong piezomagnetism in the antiferromagnetic state, observed at cryogenic temperatures below 30 kelvins.
Accordingly, the linear magnetostriction found in UO2 changes sign with the applied magnetic field and exhibits magnetoelastic memory switching phenomena at record high switch-fields of 180,000 Oe.
Due to the slow decay rate of these isotopes, it should not meaningfully influence the properties of uranium dioxide solar cells and thermoelectric devices, but it may become an important factor for VLSI chips.
The capture of alpha particles emitted during radioactive decay as helium atoms in the crystal lattice may also cause gradual long-term changes in its properties.
Uranium dioxide, like U3O8, is a ceramic material capable of withstanding high temperatures (about 2300 °C, in comparison with at most 200 °C for silicon or GaAs), making it suitable for high-temperature applications like thermophotovoltaic devices.
Uranium dioxide is also resistant to radiation damage, making it useful for rad-hard devices for special military and aerospace applications.