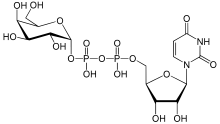
Uridine diphosphate galactose
Uridine diphosphate galactose (UDP-galactose) is an intermediate in the production of polysaccharides.
UDP-galactose is the activated form of Gal, a crucial monosaccharide building block for human milk oligosaccharide (HMO).
[2] The activated form of galactose (Gal) serves as a donor molecule involved in catalyzing the conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose.
The conversion is a rate-limiting step essential to the pace of UDP-glucose production that determines the completion of glycosylation reactions.
This compound then engages in a "ping-pong" reaction with UDP-glucose, catalyzed by uridylyltransferase, yielding glucose-1-phosphate and UDP-galactose.