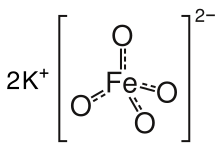
Potassium ferrate
Potassium ferrate is a powerful oxidizing agent with applications in green chemistry, organic synthesis, and cathode technology.
The combination of high temperature (200 °C - 800 °C) and oxygen presents an explosion hazard that has led many researchers to believe this method of production is not suitable from a safety viewpoint, although many attempts have been made to overcome this problem.
[3] Potassium ferrate is a dark purple crystalline solid that dissolves in water to form a reddish-purple solution.
[7] Potassium ferrate decomposes rapidly in neutral and acidic water, e.g.:[8] In alkaline solution and as a dry solid, K2FeO4 is stable.
"[13] Stabilised forms of potassium ferrate have been proposed for the removal of transuranium elements, both dissolved and suspended, from aqueous solutions.
Eckenberg and Becquerel in 1834 reported that a red-purple color appeared during heating of a mixture of potassium hydroxide and iron ore.