Beryllium oxide
This colourless solid is an electrical insulator with a higher thermal conductivity than any other non-metal except diamond, and exceeds that of most metals.
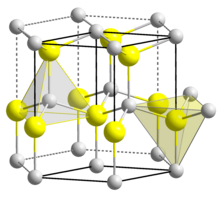
BeO crystallizes in the hexagonal wurtzite structure, featuring tetrahedral Be2+ and O2− centres, like lonsdaleite and w-BN (with both of which it is isoelectronic).
In contrast, the oxides of the larger group-2 metals, i.e., MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO, crystallize in the cubic rock salt motif with octahedral geometry about the dications and dianions.
[16] Beryllium oxide is used in rocket engines[citation needed] and as a transparent protective over-coating on aluminised telescope mirrors.
[18] It is also employed in heat sinks and spreaders that cool electronic devices, such as CPUs, lasers, and power amplifiers.
It is also used as a structural ceramic for high-performance microwave devices, vacuum tubes, cavity magnetrons [citation needed], and gas lasers.