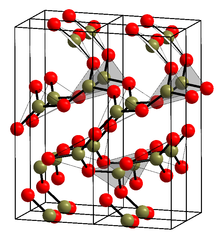
Boron trioxide
It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized only with great difficulty.
[7] It has many important industrial applications, chiefly in ceramics as a flux for glazes and enamels and in the production of glasses.
[21] Boron trioxide is produced by treating borax with sulfuric acid in a fusion furnace.
At temperatures above 750 °C, the molten boron oxide layer separates out from sodium sulfate.
Containers can be passivated internally with a graphitized carbon layer obtained by thermal decomposition of acetylene.
![Crystal structure of B2O3 [1]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d9/B2O3powder.JPG/220px-B2O3powder.JPG)