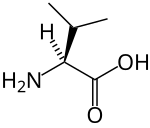
Branched-chain amino acid
[2] Synthesis for BCAAs occurs in all locations of plants, within the plastids of the cell, as determined by presence of mRNAs which encode for enzymes in the metabolic pathway.
[4] Lastly, BCAAs share the same transport protein into the brain with aromatic amino acids (Trp, Tyr, and Phe).
[4] The Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) of the U.S. Institute of Medicine set Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for essential amino acids in 2002.
Next ketoacid reductoisomerase reduces the acetohydroxy acids from the previous step to yield dihydroxyacids in both the valine and isoleucine pathways.
In a rat model of maple syrup urine disease, acute administration of BCAAs increases DNA damage in the hippocampus region of the brain.
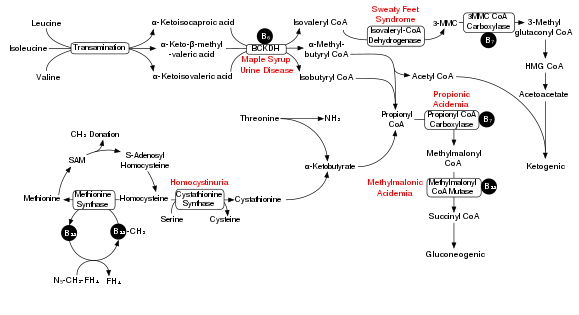
[8] The nearby Figure shows the degradation pathway of BCAAs and specifically the key role of inadequate BCKDH in maple syrup urine disease.
Leucine indirectly activates p70 S6 kinase as well as stimulates assembly of the eIF4F complex, which are essential for mRNA binding in translational initiation.
[9] P70 S6 kinase is part of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex (mTOR) signaling pathway, and has been shown to allow adaptive hypertrophy and recovery of rat muscle.
[11] Infusion of leucine at rest produces a six-hour stimulatory effect and increased protein synthesis by phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase in skeletal muscles.
[12] High glucose in the blood begins the process of the mTOR signaling pathway, in which leucine plays an indirect role.
[10][13] The combination of glucose, leucine, and other activators cause mTOR to start signaling for the proliferation of beta cells and the secretion of insulin.
Higher concentrations of leucine cause hyperactivity in the mTOR pathway, and S6 kinase is activated leading to inhibition of insulin receptor substrate through serine phosphorylation.
[14] High levels of lactic acid cause glucose metabolism to stop in order to reduce further reduction of pH.
BCAA supplementation has been shown to decrease levels of lactic acid in the muscle, allowing glucose metabolism to continue.
[18] In addition, BCAA supplementation has been shown to decrease levels of creatine kinase in muscle cells post exercise.
Creatine kinase is an indicator of muscle damage, and is responsible for transferring a phosphate group from ATP to create a phosphocreatine molecule.
[21] They can have the effect of alleviating symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy, but there is no evidence they benefit mortality rates, nutrition, or overall quality of life as further research is necessary.