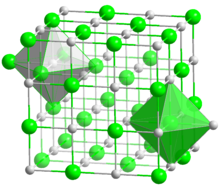
Cadmium oxide
It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers.
When pure, it is red, but CdO is unusual in being available in many differing colours due to its tendency to form defect structures resulting from anion vacancies.
[20] Cadmium oxide in the form of thin films has been used in applications such as photodiodes, phototransistors, photovoltaic cells, transparent electrodes, liquid crystal displays, IR detectors, and anti reflection coatings.
[21] CdO microparticles undergo bandgap excitation when exposed to UV-A light and is also selective in phenol photodegradation.
Brighteners are usually added to the bath and the plating is done at room temperature with high-purity cadmium anodes.