Effects of climate change
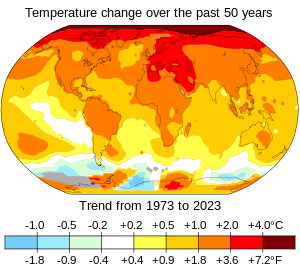
As the climate changes it impacts the natural environment with effects such as more intense forest fires, thawing permafrost, and desertification.
Ice sheets and oceans absorb the vast majority of excess heat in the atmosphere, delaying effects there but causing them to accelerate and then continue after surface temperatures stabilize.
[21] To assess changes in Earth's past climate scientists have studied tree rings, ice cores, corals, and ocean and lake sediments.
For instance such research can look at historical data for a region and conclude that a specific heat wave was more intense due to climate change.
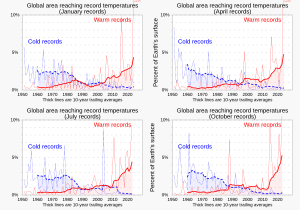
[36][37][38][39][40] As a result of changes in climatic patterns and rising global temperatures, extreme weather events like heatwaves and heavy precipitation are occurring more frequently and with increasing severity.
[51] This would lead to outbursts of very cold winter weather across parts of Eurasia[52] and North America and incursions of very warm air into the Arctic.
[53][54][55] Some stadies found a weakening of the AMOC by about 15% since 1950, causing cooling in the North Atlantic and warming in the Gulf Stream region.
[64][65][66] Atmospheric turbulence dangerous for aviation (hard to predict or that cannot be avoided by flying higher) probably increases due to climate change.
Melting ice and extreme rainfall also increase secondary hazards, particularly lahars and disturb eruption forecasting by inducing ground displacements.
Glacial earthquakes in Greenland for example, peak in frequency in the summer months and are increasing over time, possibly in response to global warming.
Earthquake sensors around the world detected the Earth's vibration but the planetary-scale of the event was so unprecedented that at first scientists failed to understand it.
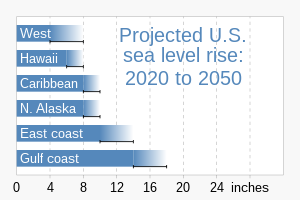
[108] The melting of the Greenland and West Antarctic ice sheets will continue to contribute to sea level rise over long time-scales.
[105]: 1215 Future melt of the West Antarctic ice sheet is potentially abrupt under a high emission scenario, as a consequence of a partial collapse.
[105]: 1269–1270 A partial collapse of the ice sheet would lead to rapid sea level rise and a local decrease in ocean salinity.
[109]: 595–596 The complete loss of the West Antarctic ice sheet would cause over 5 metres (16 ft) of sea level rise.
Movements of species to higher latitudes and altitudes,[129] changes in bird migrations, and shifting of the oceans' plankton and fish from cold- to warm-adapted communities are other impacts.
The higher frequency of droughts in the first two decades of the 21st century and other data signal that a tipping point from rainforest to savanna might be close.
[146]: 225 The climate system exhibits "threshold behavior" or tipping points when parts of the natural environment enter into a new state.
[153] A collapse of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation would likely halve rainfall in India and lead to severe drops in temperature in Northern Europe.
In coastal regions, more salt may find its way into water resources due to higher sea levels and more intense storms.
[185] Climate change is particularly likely to affect the Arctic, Africa, small islands, Asian megadeltas and the Middle East regions.
[159]: 795–796 The ten countries of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) are among the most vulnerable in the world to the negative effects of climate change.
This would happen if greenhouse gas emissions continue to grow rapidly without a change in patterns of population growth and without migration.
[206] The entire populations of small atoll nations such as Kiribati, Maldives, the Marshall Islands, and Tuvalu are at risk of being displaced.
[223] Migration due to desertification and reduced soil fertility is typically from rural areas in developing countries to towns and cities.
[231][230] Efforts to mitigate or adapt to climate change can also cause conflicts, for instance due to higher food and energy prices or when people are forcibly re-located from vulnerable areas.
To prevent it, they propose phase down fossil fuels, reduce methane emissions, overconsumption, and birth rate, switch to plant-based food, protect and restore ecosystems and adopt an ecological, post-growth economics which includes social justice.
Rising temperatures, lower water flow, and changes in rainfall could reduce total energy production by 7% annually by the end of the century.
Poor adaptation to climate change further widens the gap between what people can afford and the costs of insurance, as risks increase.
Lack of rainfall possibly linked to climate change reduced the number of ships passing through the canal per day, from 36 to 22 and by February 2024, it is expected to be 18.