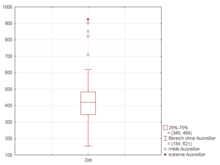
Interquartile range
[2][3][4] To calculate the IQR, the data set is divided into quartiles, or four rank-ordered even parts via linear interpolation.
The IQR is used to build box plots, simple graphical representations of a probability distribution.
[1] The quartile deviation or semi-interquartile range is defined as half the IQR.
[7] The IQR of a set of values is calculated as the difference between the upper and lower quartiles, Q3 and Q1.
For the data set in this box plot: This means the 1.5*IQR whiskers can be uneven in lengths.
The median, minimum, maximum, and the first and third quartile constitute the Five-number summary.
scores at 0.67 and −0.67 and not be normally distributed (so the above test would produce a false positive).