Inulin
Inulins are a group of naturally occurring polysaccharides produced by many types of plants,[1] industrially most often extracted from chicory.
[3] Using inulin to measure kidney function is the "gold standard" for comparison with other means of estimating glomerular filtration rate.
[4] Inulin is a natural storage carbohydrate present in more than 36,000 species of plants, including agave, wheat, onion, bananas, garlic, asparagus, Jerusalem artichoke, and chicory.
After removing the fractions with DP lower than 10 during manufacturing process, the remaining product is high-performance inulin.
[5][6] Some articles considered the fractions with DP lower than 10 as short-chained fructo-oligosaccharides, and only called the longer-chained molecules inulin.
[7] Because of the β(2,1) linkages, inulin is not digested by enzymes in the human alimentary system, contributing to its functional properties: reduced calorie value, dietary fiber, and prebiotic effects.
When thoroughly mixed with liquid, inulin forms a gel and a white creamy structure, which is similar to fat.
Its three-dimensional gel network, consisting of insoluble submicron crystalline inulin particles, immobilizes a large amount of water, assuring its physical stability.
[5] After harvest, the chicory roots are sliced and washed, then soaked in a solvent (hot water or ethanol);[16] the inulin is then isolated, purified, and spray dried.
[18] In the early 21st century, the use of inulin in processed foods was due in part to its adaptable characteristics for manufacturing.
[19] Although FODMAPs may cause certain digestive discomfort in some people, they produce potentially favorable alterations in the intestinal flora that contribute to maintaining health of the colon.
[32] A 2017 systematic review of low-to-moderate quality clinical trial research showed that dietary supplementation with inulin-type fructans reduced blood levels of low-density cholesterol, a biomarker of cardiovascular disease.
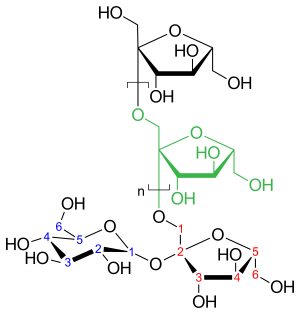
[36] Inulins are polymers composed mainly of fructose units (fructans), and typically have a terminal glucose.
Inulin is uniquely treated by nephrons in that it is completely filtered at the glomerulus but neither secreted nor reabsorbed by the tubules.
PAH is partially filtered from plasma at the glomerulus and not reabsorbed by the tubules, in a manner identical to inulin.
Only in the colon do bacteria metabolise inulin with the release of significant quantities of carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and/or methane.
[40] Because normal digestion does not break inulin down into monosaccharides, it does not elevate blood sugar levels and may therefore be helpful in the management of diabetes.
[41] Many foods naturally high in inulin or fructo-oligosaccharides such as chicory, garlic, and leek have been seen as "stimulants of good health" for centuries.