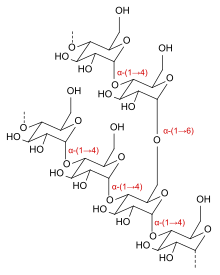
Dextrin
Dextrins can be produced from starch using enzymes like amylases, as during digestion in the human body and during malting and mashing in beer brewing[3] or by applying dry heat under acidic conditions (pyrolysis or roasting).
Dextrins are white, yellow, or brown powders that are partially or fully water-soluble, yielding optically active solutions of low viscosity.
White and yellow dextrins from starch roasted with little or no acid are called British gum.
Indigestible dextrins have been developed as soluble stand-alone fiber supplements and for adding to processed food products.
It is also produced by enzymatic hydrolysis from gelled starch, and is usually found as a creamy-white hygroscopic spray-dried powder.