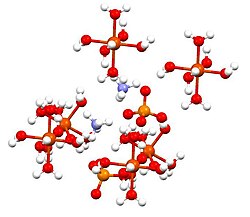
Ammonium iron(II) sulfate
Ammonium iron(II) sulfate, or Mohr's salt, is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2SO4·Fe(SO4)·6H2O.
This compound is a member of a group of double sulfates called Schönites or Tutton's salts.
In analytical chemistry, this salt is the preferred source of ferrous ions as the solid has a long shelf life, being resistant to oxidation.
The ammonium ions make solutions of Mohr's salt slightly acidic, which slows this oxidation process.
[5] Common impurities include magnesium, nickel, manganese, lead, and zinc, many of which form isomorphous salts.