Potentiometer (measuring instrument)
At that point the galvanometer draws no current from the unknown source, and the magnitude of voltage can be calculated from the position of the sliding contact.
This null balance measuring method is still important in electrical metrology and standards work and is also used in other areas of electronics.
The principle of a potentiometer is that the potential dropped across a segment of a wire of uniform cross-section carrying a constant current is directly proportional to its length.
One form of potentiometer is a uniform high-resistance wire attached to an insulating support, marked with a linear measuring scale.
In use, an adjustable regulated voltage source E, of greater magnitude than the potential to be measured, is connected across the wire so as to pass a steady current through it.
In this circuit, the ends of a uniform resistance wire R1 are connected to a regulated DC supply VS for use as a voltage divider.
The potentiometer is first calibrated by positioning the wiper (arrow) at the spot on the R1 wire that corresponds to the voltage of a standard cell so that
An unknown DC voltage, in series with the galvanometer, is then connected to the sliding wiper, across a variable-length section R3 of the resistance wire.
Because the resistance wire can be made very uniform in cross-section and resistivity, and the position of the wiper can be measured easily, this method can be used to measure unknown DC voltages greater than or less than a calibration voltage produced by a standard cell without drawing any current from the standard cell.
The constant resistance potentiometer is a variation of the basic idea in which a variable current is fed through a fixed resistor.
A metre bridge is a simple type of potentiometer which may be used in school science laboratories to demonstrate the principle of resistance measurement by potentiometric means.

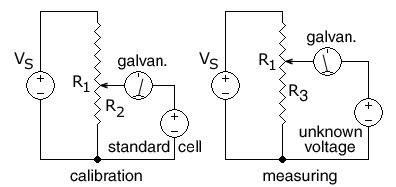
R 1 is the resistance of the entire resistance wire. The arrow head represents the moving wiper .