World War I
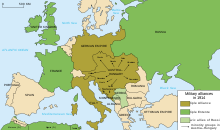
The causes of World War I included the rise of Germany and decline of the Ottoman Empire, which disturbed the long-standing balance of power in Europe, as well as economic competition between nations triggered by industrialisation and imperialism.
Growing tensions between the great powers and in the Balkans reached a breaking point on 28 June 1914, when a Bosnian Serb named Gavrilo Princip assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne.
Germany's strategy in 1914 was to quickly defeat France then transfer its forces to the east, but its advance was halted in September, and by the end of the year the Western Front consisted of a continuous line of trenches stretching from the English Channel to Switzerland.
The Paris Peace Conference of 1919–1920 imposed settlements on the defeated powers, most notably the Treaty of Versailles, by which Germany lost significant territories, was disarmed, and was required to pay large war reparations to the Allies.
[14] This policy was based on the work of US naval author Alfred Thayer Mahan, who argued that possession of a blue-water navy was vital for global power projection; Tirpitz had his books translated into German, while Wilhelm made them required reading for his advisors and senior military personnel.
Bismarck thought that the British would not interfere in Europe, as long as its maritime supremacy remained secure, but his dismissal in 1890 led to a change in policy and an Anglo-German naval arms race began.
After Germany expanded its standing army by 170,000 troops in 1913, France extended compulsory military service from two to three years; similar measures were taken by the Balkan powers and Italy, which led to increased expenditure by the Ottomans and Austria-Hungary.
[25] The result was that even countries which benefited from the Balkan Wars, such as Serbia and Greece, felt cheated of their "rightful gains", while for Austria it demonstrated the apparent indifference with which other powers viewed their concerns, including Germany.
Cvjetko Popović, Gavrilo Princip, Nedeljko Čabrinović, Trifko Grabež, Vaso Čubrilović (Bosnian Serbs) and Muhamed Mehmedbašić (from the Bosniaks community),[33] from the movement known as Young Bosnia, took up positions along the Archduke's motorcade route, to assassinate him.
Rather than a direct attack across their shared frontier, the German right wing would sweep through the Netherlands and Belgium, then swing south, encircling Paris and trapping the French army against the Swiss border.
[81] The suffering engendered by the war, as well as the failure of the British government to grant self-government to India afterward, bred disillusionment, resulting in the campaign for full independence led by Mahatma Gandhi.
This tactic made it difficult for U-boats to find targets, which significantly lessened losses; after the hydrophone and depth charges were introduced, destroyers could potentially successfully attack a submerged submarine.
[104] World War I also saw the first use of aircraft carriers in combat, with HMS Furious launching Sopwith Camels in a successful raid against the Zeppelin hangars at Tondern in July 1918, as well as blimps for antisubmarine patrol.
[134] The advantage of superior numbers was offset by the difficult terrain; much of the fighting took place high in the Alps and Dolomites, where trench lines had to be cut through rock and ice and keeping troops supplied was a major challenge.
Although their attack on Galicia was largely successful, and the invasions achieved their aim of forcing Germany to divert troops from the Western Front, the speed of mobilisation meant they did so without much of their heavy equipment and support functions.
[150] With the ruling elite split into pro-German and pro-Entente factions,[151] Romania remained neutral for two years while allowing Germany and Austria to transport military supplies and advisors across Romanian territory.
[152] In September 1914, Russia acknowledged Romanian rights to Austro-Hungarian territories including Transylvania and Banat, whose acquisition had widespread popular support,[150] and Russian success against Austria led Romania to join the Entente in the August 1916 Treaty of Bucharest.
[153] On 27 August 1916, they attacked Transylvania and occupied substantial parts of the province before being driven back by the recently formed German 9th Army, led by former Chief of Staff Erich von Falkenhayn.
[156] Following the Russian revolution, Romania found itself alone on the Eastern Front and signed the Treaty of Bucharest with the Central Powers, which recognised Romanian sovereignty over Bessarabia in return for ceding control of passes in the Carpathian Mountains to Austria-Hungary and leasing its oil wells to Germany.
[163] Revolutionaries set up the Petrograd Soviet and fearing a left-wing takeover, the State Duma forced Nicholas to abdicate and established the Russian Provisional Government, which confirmed Russia's willingness to continue the war.
[171] Despite his conviction that Germany must be defeated, Wilson went to war to ensure the US played a leading role in shaping the peace, which meant preserving the AEF as a separate military force, rather than being absorbed into British or French units as his Allies wanted.
[172] He was strongly supported by AEF commander General John J. Pershing, a proponent of pre-1914 "open warfare" who considered the French and British emphasis on artillery misguided and incompatible with American "offensive spirit".
[174] In December 1916, Robert Nivelle replaced Pétain as commander of French armies on the Western Front and began planning a spring attack in Champagne, part of a joint Franco-British operation.
[175] Poor security meant German intelligence was well informed on tactics and timetables, but despite this, when the attack began on 16 April the French made substantial gains, before being brought to a halt by the newly built and extremely strong defences of the Hindenburg Line.
The following week, cooperating American and French units broke through in Champagne at the Battle of Blanc Mont Ridge (3–27 October), forcing the Germans off the commanding heights, and closing towards the Belgian frontier.
[204][205] On the same day, the German Supreme Army Command informed Wilhelm II and the Imperial Chancellor Count Georg von Hertling, that the military situation facing Germany was hopeless.
The sailors' revolt, which then ensued in the naval ports of Wilhelmshaven and Kiel, spread across the whole country within days and led to the proclamation of a republic on 9 November 1918, shortly thereafter to the abdication of Wilhelm II, and German surrender.
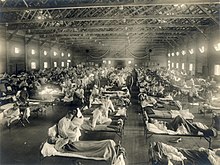
[251] Starting in early 1918, a major influenza epidemic known as Spanish flu spread across the world, accelerated by the movement of large numbers of soldiers, often crammed together in camps and transport ships with poor sanitation.
[263][266] The government of Turkey continues to deny the genocide to the present day, arguing that those who died were victims of inter-ethnic fighting, famine, or disease during World War I; these claims are rejected by most historians.
[303] Von Syburg, the German envoy in Addis Ababa, said, "now the time has come for Ethiopia to regain the coast of the Red Sea driving the Italians home, to restore the Empire to its ancient size."