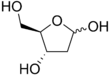
Deoxyribose
Several isomers exist with the formula H−(C=O)−(CH2)−(CHOH)3−H, but in deoxyribose all the hydroxyl groups are on the same side in the Fischer projection.
[6] The DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule, which is the main repository of genetic information in life, consists of a long chain of deoxyribose-containing units called nucleotides, linked via phosphate groups.
In the standard nucleic acid nomenclature, a DNA nucleotide consists of a deoxyribose molecule with an organic base (usually adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine) attached to the 1′ ribose carbon.
The absence of the 2′ hydroxyl group in deoxyribose is apparently responsible for the increased mechanical flexibility of DNA compared to RNA, which allows it to assume the double-helix conformation, and also (in the eukaryotes) to be compactly coiled within the small cell nucleus.
Other biologically important derivatives of deoxyribose include mono-, di-, and triphosphates, as well as 3′-5′ cyclic monophosphates.