Engineering
Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include designing and improving infrastructure, machinery, vehicles, electronics, materials, and energy systems.
The word "engine" itself is of even older origin, ultimately deriving from the Latin ingenium (c. 1250), meaning "innate quality, especially mental power, hence a clever invention.
Other monuments, no longer standing, such as the Hanging Gardens of Babylon and the Pharos of Alexandria, were important engineering achievements of their time and were considered among the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
[10] The lever mechanism first appeared around 5,000 years ago in the Near East, where it was used in a simple balance scale,[11] and to move large objects in ancient Egyptian technology.
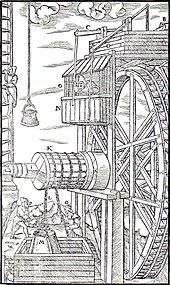
[18] The earliest practical water-powered machines, the water wheel and watermill, first appeared in the Persian Empire, in what are now Iraq and Iran, by the early 4th century BC.
[32] The earliest practical wind-powered machines, the windmill and wind pump, first appeared in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age, in what are now Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, by the 9th century AD.
The first music sequencer was an automated flute player invented by the Banu Musa brothers, described in their Book of Ingenious Devices, in the 9th century.
Using a model water wheel, Smeaton conducted experiments for seven years, determining ways to increase efficiency.
The sequence of events began with the invention of the barometer and the measurement of atmospheric pressure by Evangelista Torricelli in 1643, demonstration of the force of atmospheric pressure by Otto von Guericke using the Magdeburg hemispheres in 1656, laboratory experiments by Denis Papin, who built experimental model steam engines and demonstrated the use of a piston, which he published in 1707.
Edward Somerset, 2nd Marquess of Worcester published a book of 100 inventions containing a method for raising waters similar to a coffee percolator.
Hot blast, patented by James Beaumont Neilson in 1828, greatly lowered the amount of fuel needed to smelt iron.
The Industrial Revolution created a demand for machinery with metal parts, which led to the development of several machine tools.
Civil engineering is the design and construction of public and private works, such as infrastructure (airports, roads, railways, water supply, and treatment etc.
Aerospace engineering covers the design, development, manufacture and operational behaviour of aircraft, satellites and rockets.
Examples of bioengineering research include bacteria engineered to produce chemicals, new medical imaging technology, portable and rapid disease diagnostic devices, prosthetics, biopharmaceuticals, and tissue-engineered organs.
Geological engineers are involved with impact studies for facilities and operations that affect surface and subsurface environments, such as rock excavations (e.g. tunnels), building foundation consolidation, slope and fill stabilization, landslide risk assessment, groundwater monitoring, groundwater remediation, mining excavations, and natural resource exploration.
Marine engineering covers the design, development, manufacture and operational behaviour of watercraft and stationary structures like oil platforms and ports.
The task of the engineer is to identify, understand, and interpret the constraints on a design in order to yield a successful result.
Constraints may include available resources, physical, imaginative or technical limitations, flexibility for future modifications and additions, and other factors, such as requirements for cost, safety, marketability, productivity, and serviceability.
[71] Engineers take on the responsibility of producing designs that will perform as well as expected and, except those employed in specific areas of the arms industry, will not harm people.
These allow products and components to be checked for flaws; assess fit and assembly; study ergonomics; and to analyze static and dynamic characteristics of systems such as stresses, temperatures, electromagnetic emissions, electrical currents and voltages, digital logic levels, fluid flows, and kinematics.
In recent years the use of computer software to aid the development of goods has collectively come to be known as product lifecycle management (PLM).
Examples from different engineering disciplines include: the development of nuclear weapons, the Three Gorges Dam, the design and use of sport utility vehicles and the extraction of oil.
Accordingly, the services provided by engineers require honesty, impartiality, fairness, and equity, and must be dedicated to the protection of the public health, safety, and welfare.
[95] An example of this is the use of numerical approximations to the Navier–Stokes equations to describe aerodynamic flow over an aircraft, or the use of the finite element method to calculate the stresses in complex components.
That something can be a complex system, device, a gadget, a material, a method, a computing program, an innovative experiment, a new solution to a problem, or an improvement on what already exists.
This often requires moving forward before phenomena are completely understood in a more rigorous scientific sense and therefore experimentation and empirical knowledge is an integral part of both.
[103] The heart for example functions much like a pump,[104] the skeleton is like a linked structure with levers,[105] the brain produces electrical signals etc.
Engineers specializing in change management must have in-depth knowledge of the application of industrial and organizational psychology principles and methods.
This work often deals with large scale complex business transformation or business process management initiatives in aerospace and defence, automotive, oil and gas, machinery, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, electrical and electronics, power distribution and generation, utilities and transportation systems.