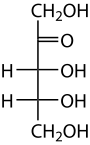
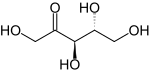
Ribulose
Ribulose is a ketopentose — a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including a ketone functional group.
Ribulose sugars are composed in the pentose phosphate pathway from arabinose.
For example, d-ribulose is an intermediate in the fungal pathway for d-arabitol production.
Also, as the 1,5-bisphosphate, d-ribulose combines with carbon dioxide at the start of the photosynthesis process in green plants (carbon dioxide trap).
[2] Ribulose has the same stereochemistry at carbons 3 and 4 as the five-carbon aldoses ribose and arabinose.