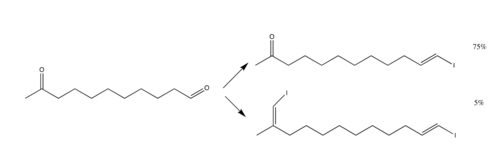
Takai olefination
[1] In the original reaction, the organochromium species is generated from iodoform or bromoform and an excess of chromium(II) chloride and the product is a vinyl halide.
[4] Prior to the introduction of this chromium-based protocol, olefination reactions generally gave Z alkenes or mixtures of isomers.
[6] To circumvent this issue, the Takai group examined the synthetic potential of chromium(II) salts.
[1] The drawbacks to the reaction include the fact that stoichiometrically, four equivalents of chromium chloride must be used, since there is a reduction of two halogen atoms.
[3] Ways to limit the amount of chromium chloride exist, namely by utilization of zinc equivalent,[7] but this method remains unpopular.