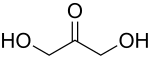
Triose
A triose is a monosaccharide, or simple sugar, containing three carbon atoms.
There are only three possible trioses: the two enantiomers of glyceraldehyde, which are aldoses; and dihydroxyacetone, a ketose which is symmetrical and therefore has no enantiomers.
[1] Trioses are important in cellular respiration.
During glycolysis, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is broken down into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
[2] Importance of Triose in the Body