Late modern period
The captaincies they created were subdued to a centralized administration in Salvador (later relocated to Rio de Janeiro) which reported directly to the Portuguese Crown until its independence in 1822, becoming the Empire of Brazil.
[citation needed] British imperial strength was underpinned by the steamship and the telegraph, new technologies invented in the second half of the 19th century, allowing it to control and defend the Empire.
[citation needed] The Antebellum Age was a period of increasing division in the country based on the growth of slavery in the American South and in the western territories of Kansas and Nebraska that eventually led to the Civil War in 1861.
[citation needed] "Manifest destiny" was the belief that the United States was destined to expand across the North American continent, from the Atlantic seaboard to the Pacific Ocean.
[citation needed] During the Gilded Age, there was substantial growth in population in the United States and extravagant displays of wealth and excess of America's upper-class during the post-Civil War and post-Reconstruction era, in the late 19th century.
These ideas were challenged, for example by the young Karl Marx, who criticized the project of political emancipation (embodied in the form of human rights), asserting it to be symptomatic of the very dehumanization it was supposed to oppose.
He also made important contributions to statistical mechanics, especially his mathematical treatment of Brownian motion, his resolution of the paradox of specific heats, and his connection of fluctuations and dissipation.
Responding to these civil failures and discontent, the Qing Imperial Court did attempt to reform the government in various ways, as the decision to draft a constitution in 1906, the establishment of provincial legislatures in 1909, and the preparation for a national parliament in 1910.
To prevent civil war and possible foreign intervention from undermining the infant republic, leaders agreed to the army's demand that China be united under a Beijing government.
These victories, as time transpired, would dramatically transform the distribution of power in East Asia, resulting in a reassessment of Japan's recent entry onto the world stage.
[citation needed] The Edwardian era in the United Kingdom is the period spanning the reign of King Edward VII up to the end of the First World War, including the years surrounding the sinking of the RMS Titanic.
The immediate origins of the war lay in the decisions taken by statesmen and generals during the July Crisis of 1914, the spark (or casus belli) for which was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria.
[citation needed] However, the crisis did not exist in a void; it came after a long series of diplomatic clashes between the Great Powers over European and colonial issues in the decade prior to 1914 which had left tensions high.
More than 9 million soldiers died on the various battlefields, and nearly that many more in the participating countries' home fronts on account of food shortages and genocide committed under the cover of various civil wars and internal conflicts.
The unsanitary conditions engendered by the war, severe overcrowding in barracks, wartime propaganda interfering with public health warnings, and migration of so many soldiers around the world helped the outbreak become a pandemic.
Vladimir Lenin's decision has been attributed to his sponsorship by the foreign office of Wilhelm II, German Emperor, offered by the latter in hopes that with a revolution, Russia would withdraw from World War I.
The Western Allies expressed their dismay at the Bolsheviks, upset at:[citation needed] In addition, there was a concern, shared by many Central Powers as well, that the socialist revolutionary ideas would spread to the West.
[citation needed] While the early 1920s was a time of flux for revolutionary Russia and Central Asia, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics was proclaimed in 1922 as the successor state to the fallen Russian Empire.
But for political expediency, the Soviet leadership initiated a dual policy of support for both Sun and the newly established Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
But Chiang Kai-shek, whose Northern Expedition was proving successful, set his forces to destroying the Shanghai CCP apparatus and established an anti-Communist government at Nanjing in April 1927.
[citation needed] The "Nanjing Decade" of 1928–37 was one of consolidation and accomplishment under the leadership of the Nationalists, with a mixed but generally positive record in the economy, social progress, development of democracy, and cultural creativity.
The 1920s was further distinguished by several inventions and discoveries, extensive industrial growth and the rise in consumer demand and aspirations, and significant changes in lifestyle.Europe spent these years rebuilding and coming to terms with the vast human cost of the conflict.
In Germany, the Weimar Republic gave way to episodes of political and economic turmoil, which culminated with the German hyperinflation of 1923 and the failed Beer Hall Putsch of that same year.
[citation needed] A series of international crises strained the League to its limits, the earliest being the invasion of Manchuria by Japan and the Abyssinian crisis of 1935/36 in which Italy invaded Abyssinia, one of the only free African nations at that time.
[citation needed] Facing resource scarcity due to a growing population, Japan seized Manchuria in September 1931 and put ex-Qing emperor Puyi in charge as head of the puppet state of Manchukuo in 1932.
The Japanese were faced with the option of either withdrawing from China or seizing and securing new sources of raw materials in the resource-rich, European-controlled colonies of Southeast Asia—specifically British Malaya and the Dutch East Indies (modern-day Indonesia).
The Allies were initially made up of Poland, the United Kingdom, France, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, South Africa, as well as British Commonwealth countries which were controlled directly by the UK, such as the Indian Empire.
[citation needed] The Holocaust (which roughly means "burnt whole") was the deliberate and systematic murder of millions of Jews and other "unwanted" during World War II by the Nazi regime in Germany.
Many economists made the case that this understated the magnitude of growth, as many of the goods and services consumed at the end of the 20th century, such as improved medicine (causing world life expectancy to increase by more than two decades) and communications technologies, were not available at any price at its inception.
[63] In Latin America in the 1970s, leftists acquired a significant political influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a large portion of the individual country's upper class to support coups d'état to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat.


















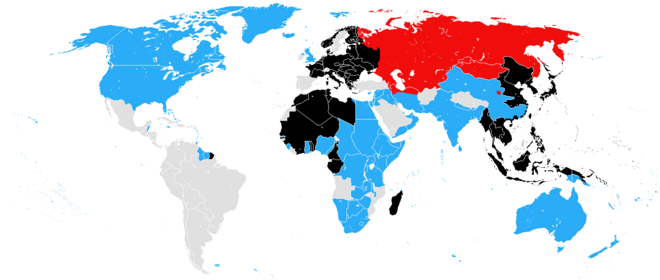
Allied powers and areas
Central powers and colonies or occupied territory
Neutral countries