History of Western civilization
The West invented cinema, television, radio, telephone, the automobile, rocketry, flight, electric light, the personal computer and the Internet; produced artists such as Michelangelo, Shakespeare, Leonardo da Vinci, Beethoven, Vincent van Gogh, Picasso, Bach and Mozart; developed sports such as soccer, cricket, golf, tennis, rugby and basketball; and transported humans to an astronomical object for the first time with the 1969 Apollo 11 Moon Landing.
[13] According to art historian Kenneth Clark, for some five centuries after the fall of Rome, virtually all men of intellect joined the Church and practically nobody in western Europe outside of monastic settlements had the ability to read or write.
Working as a trader he encountered the ideas of Christianity and Judaism on the fringes of the Byzantine Empire, and around 610 began preaching of a new monotheistic religion, Islam, and in 622 became the civil and spiritual leader of Medina, soon after conquering Mecca in 630.
Monumental abbeys and cathedrals were constructed and decorated with sculptures, hangings, mosaics and works belonging to one of the greatest epochs of art and providing stark contrast to the monotonous and cramped conditions of ordinary living.
Abbot Suger of the Abbey of St. Denis is considered an influential early patron of Gothic architecture and believed that love of beauty brought people closer to God: "The dull mind rises to truth through that which is material".
[37] However, in 1378 the breakdown in relations between the cardinals and Gregory's successor, Urban VI, gave rise to the Western Schism – which saw another line of Avignon Popes set up as rivals to Rome (subsequent Catholic history does not grant them legitimacy).
While art and architecture flourished in Italy and then the Netherlands, religious reformers flowered in Germany and Switzerland; printing was establishing itself in the Rhineland and navigators were embarking on extraordinary voyages of discovery from Portugal and Spain.
Important thinkers of the Renaissance in Northern Europe included the Catholic humanists Desiderius Erasmus, a Dutch theologian, and the English statesman and philosopher Thomas More, who wrote the seminal work Utopia in 1516.
As the calendar reached the year 1500, Europe was blossoming – with Leonardo da Vinci painting his Mona Lisa portrait not long after Christopher Columbus reached the Americas (1492), Amerigo Vespucci proved that America is not a part of India, the Portuguese navigator Vasco Da Gama sailed around Africa into the Indian Ocean and Michelangelo completed his paintings of Old Testament themes on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel in Rome (the expense of such artistic exuberance did much to spur the likes of Martin Luther in Northern Europe in their protests against the Church of Rome).
In Spain Miguel de Cervantes wrote the novel Don Quixote, other important works of literature in this period were the Canterbury Tales by Geoffrey Chaucer and Le Morte d'Arthur by Sir Thomas Malory.
The Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama led the first sailing expedition directly from Europe to India in 1497–1499, by the Atlantic and Indian oceans, opening up the possibility of trade with the East other than via perilous overland routes like the Silk Road.
Ruled by the Protestant Ascendancy, Ireland eventually became an English-speaking land, though the majority population preserved distinct cultural and religious outlooks, remaining predomininantly Catholic except in parts of Ulster and Dublin.
It was famous for its rare quasi-democratic political system, praised by philosophers such as Erasmus; and, during the Counter-Reformation, was known for near-unparalleled religious tolerance, with peacefully coexisting Catholic, Jewish, Eastern Orthodox, Protestant and Muslim communities.
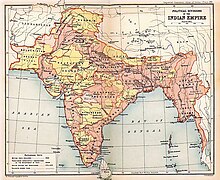
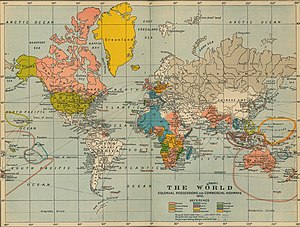
It consolidated control over such far flung territories as Canada and Jamaica in the Americas, Australia and New Zealand in Oceania; Malaya, Hong Kong and Singapore in the Far East and a line of colonial possessions from Egypt to the Cape of Good Hope through Africa.
While remaining a minority religion in the British Empire, a steady stream of new Catholics would continue to convert from the Church of England and Ireland, notably John Henry Newman and the poets Gerard Manley Hopkins and Oscar Wilde.
The 1859 publication of On the Origin of Species, by the English naturalist Charles Darwin, provided an alternative hypothesis for the development, diversification, and design of human life to the traditional poetic scriptural explanation known as Creationism.
Among the greatest Romantic artists were Eugène Delacroix, Francisco Goya, Karl Bryullov, J. M. W. Turner, John Constable, Caspar David Friedrich, Ivan Aivazovsky, Thomas Cole, and William Blake.
[92] Romantic poetry emerged as a significant genre, particularly during the Victorian Era with leading exponents including William Wordsworth, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Robert Burns, Edgar Allan Poe and John Keats.
The great Realist painters include Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin, Gustave Courbet, Jean-François Millet, Camille Corot, Honoré Daumier, Édouard Manet, Edgar Degas (both considered as Impressionists), Ilya Repin, and Thomas Eakins, among others.
Leo Tolstoy (War and Peace, Anna Karenina) and Fyodor Dostoevsky (Crime and Punishment, The Idiot, The Brothers Karamazov) soon became internationally renowned to the point that many scholars such as F. R. Leavis have described one or the other as the greatest novelist ever.
[114] The Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, stated that Britain and its dominions were "equal in status, in no way subordinate one to another in any aspect of their domestic or external affairs, though united by common allegiance to the Crown, and freely associated as members of the British Commonwealth of Nations".
In 1936, a military coup d'état against the republic started the Spanish Civil War, which ended in 1939 with the victory of the rebel side (supported by Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany), and with Francisco Franco as dictator.
U.S. General Douglas MacArthur, based in Melbourne, Australia became "Supreme Allied Commander of the South West Pacific" and the foundations of the post war Australia-New Zealand-United States Alliance were laid.
Fearing a land invasion would cost one million American lives, the U.S. used a new weapon against Japan, the atomic bomb, developed after years of work by an international team including Germans, in the United States.
Firstly, World War II had devastated European economies and had forced governments to spend great deals of money, making the price of colonial administration increasingly hard to manage.
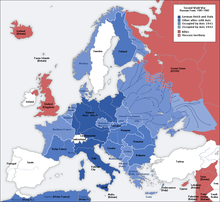
In the years following World War II, the Soviets established satellite states throughout Central and Eastern Europe, including historically and culturally Western nations like Poland and Hungary.
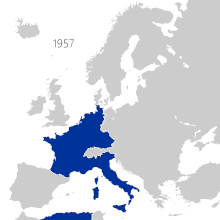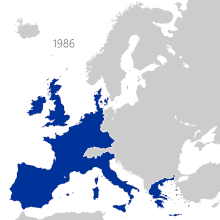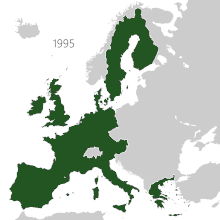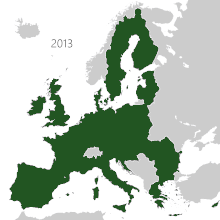
[citation needed] Between 1945 and 1980, the British Empire was transformed from its centuries old position as a global colonial power, to a voluntary association known as the Commonwealth of Nations – only some of which retained any formal political links to Britain or its monarchy.
The Maori and Australian Aborigines had been largely dispossessed and disenfranchised during the 19th and early 20th centuries, but relations between the descendants of European settlers and the Indigenous peoples of Australia and New Zealand began to improve through legislative and social reform over the post-war period corresponding with the civil rights movement in North America.
Yeltsin's chosen successor, the former spy, Vladimir Putin, tightened the reins on political opposition, opposed separatist movements within the Russian Federation, and battled pro-Western neighbour states like Georgia, contributing to a challenging climate of relations with Europe and America.
Nevertheless, in a sign of the continuing status of the ancient Western institution of the Papacy in the early 21st century, the Funeral of Pope John Paul II brought together the single largest gathering in history of heads of state outside the United Nations.